Autism Spectrum Test
You are here because one of your friends linked you to their Autism Spectrum Test result:
Take the TestResults:
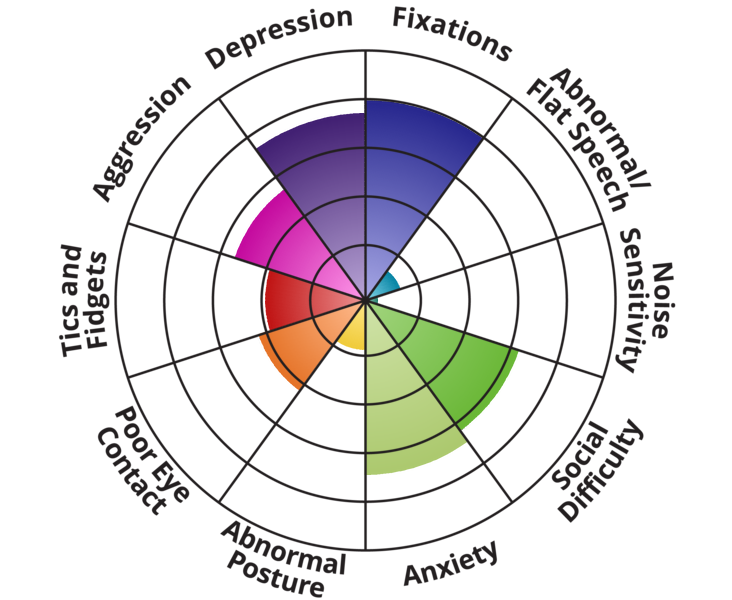
Your friend's autism spectrum symptoms are moderate.
Take the TestExplanation of Facets:
Depression: People with autism are four times more likely to experience depression than those who are neurotypical. One of the strongest predictors of depression is loneliness. Since individuals high in the autism spectrum are more at risk of isolating themselves, they may have more depression triggers.
Fixations: Many people with autism spectrum disorders have difficulties in dealing with change. As a consequence, they often have routines that they feel that they need to follow. Adhering to these rituals and routines tends to make them feel more in control of their environment. They also usually have special interests that they feel they must tend to, which they experience as fundamental to their well-being.
Abnormal/Flat Speech: Individuals with autism generally speak differently from most people. They may talk in a flat or exaggerated way or speak in clipped bursts. This relates to the general difficulties people with autism spectrum disorders experience in understanding metaphors, social cues, and the subtexts of certain words.
Noise Sensitivity: One common symptom experienced by people with autism spectrum disorders is intense sensitivity to sound. Autism spectrum individuals may be easily overwhelmed by noises as well as other environmental stimuli such as abnormal temperatures or lights.
Social Difficulty: Many individuals on the autism spectrum feel challenged when it comes to making or engaging friends and may be overwhelmed by uncertain social situations. This disposition is often related to their difficulties with reading non-verbal communication, or, conversely, to their own adherence to fixed routines or tendency towards flat speech.
Anxiety: Individuals with autism often develop irrational fears or phobias, social anxiety, and separation anxiety. They may struggle with intense levels of stress due to their sensory sensitivities and/or difficulties adapting to changes in their routines. Individuals high in Social Anxiety may also develop a fear of negative reactions from their peers.
Abnormal Posture: Individuals on the autism spectrum often struggle with a reduced perception of their bodily movements. As a result, they may have difficulties with their motor coordination or postural orientation. These tendencies may further exacerbate their social isolation.
Poor Eye Contact: One of the hallmarks of autism is the tendency to avoid eye contact. Individuals on the autism spectrum often find that maintaining eye contact causes them stress. Due to the overwhelming sensory input many experience, many individuals with autism would rather look at something else, such as static objects or another person’s shoes.
Tics and Fidgets: Individuals with autism may experience motoric and somatic tics such as head movements, excessive blinking, or twitching. They may also struggle with vocal tics, such as repeating words or phrases. Finally, some find it challenging to keep still, and they constantly feel the urge to fidget.
Aggression: Some individuals with autism may be prone to aggression in the form of hitting objects or things, destroying property, and/or throwing temper tantrums. This is especially likely to occur for those individuals with autism who cannot speak well, as this is another way of communicating their needs.
References
- Barret, S., Uljarevic, M., Baker, E., Richdale, A., Jones, C., & Leekam, S. (2015). The adult repetitive behaviours questionnaire-2 (RBQ-2A): A self-report measure of restricted and repetitive behaviours. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(11): 3680–3692.
- Barrett, S.L., Uljarević, M., Jones, C.R.G. et al. Assessing subtypes of restricted and repetitive behaviour using the Adult Repetitive Behaviour Questionnaire-2 in autistic adults. Molecular Autism 9, 58 (2018).
- Allely, C.S. (2019). Exploring the female autism phenotype of repetitive behaviours and restricted interests: A systematic PRISMA review. University of Salford Institutional Repository.
Take Next
GET THE FULL STORY
Become a lifetime member with a one-time payment
WHAT YOU GET
Access to members-only tests
Ability to track and save test results
Access to all of our eBooks (value $44.94)
Access to premium type assessments and infographics
Become a memberGET THE FULL STORY
Living Autistic
WHAT YOU GET
78-page manual, explaining the typical challenges and paths to growth experienced by people with autistic traits.
Presented in an easy-to-read style and written by people who have grappled with these challenges themselves.
14-day, no-questions-asked, money-back guarantee.
Order NowGET THE FULL STORY
Manual of Personality Styles
WHAT YOU GET
71-page manual, explaining the make-up of all personality styles, their hidden drives, and the theory behind the system.
Presented in an easy-to-read style and backed up by solid academic references.
14-day, no-questions-asked, money-back guarantee.
Order NowSave and monitor your results over time
Become a member today
Sign Up












